Born July 14, 1868 Baden bei Wien (close Vienna), Austria-Hungary Died June 26, 1943 (matured 75) New York City, New York, U....
Born July 14, 1868
Baden bei Wien (close Vienna), Austria-Hungary
Died June 26, 1943 (matured 75)
New York City, New York, U.S.
Residence Austria
Joined States of America
Citizenship Austrian - American
Nationality Austrian
Fields Medicine, virology
Institutions University of Vienna
Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research, New York
Alma mater University of Vienna
Known for Development of blood gathering, disclosure of Rh component, revelation of poliovirus
Striking recompenses
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1930)
Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award (1946 after death)
ForMemRS (1941)
Karl Landsteiner
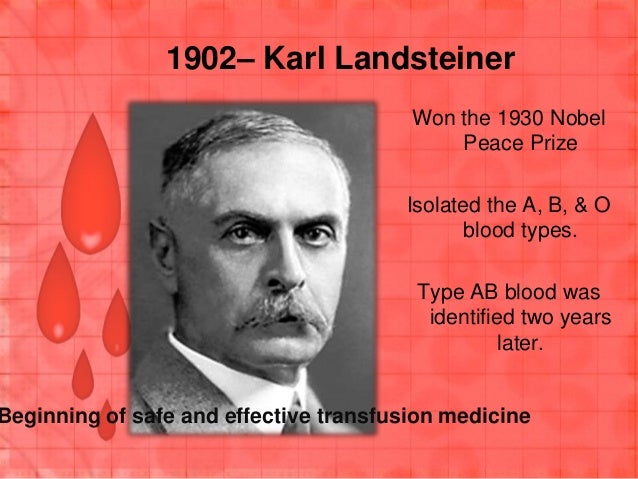
Karl Landsteiner, ForMemRS (June 14, 1868 – June 26, 1943), was an Austrian and American scientist and physician. He is noted for having initially recognized the fundamental blood bunches in 1900, having built up the advanced arrangement of characterization of blood gatherings from his ID of the nearness of agglutinins in the blood, and having distinguished, with Alexander S. Wiener, the Rhesus variable, in 1937, subsequently empowering doctors to transfuse blood without jeopardizing the patient′s life. With Constantin Levaditi and Erwin Popper, he found the polio infection in 1909. He got the Aronson Prize and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. He was honored a Lasker Award in 1946 after death and is perceived as the father of transfusion medication.Discovery of the blood groups
In 1900 Karl Landsteiner discovered that the blood of two individuals under contact agglutinates, and in 1901 he found that this impact was because of contact of blood with blood serum. Subsequently, he succeeded in distinguishing the three blood amasses A, B and O, which he named C, of human blood. Landsteiner additionally discovered that blood transfusion between persons with the same blood bunch did not prompt the demolition of platelets, though this happened between persons of various blood groups.Based on his discoveries, the first an effective blood transfusion was performed by Reuben Ottenberg at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York in 1907.
Awards and honours
Landsteiner was after death granted the Lasker-DeBakey Clinical Medical Research Award in 1946 and chose a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 1941. He got the Aronson Prize in 1926. In 1930, he got the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. He was recompensed with Lasker Award in 1946 after death and is perceived as the father of transfusion medicine. On fourteenth June 2016, Google demonstrated a Doodle for the 148th birthday of Karl Landsteiner.





 #ref-menu
#ref-menu #ref-menu
#ref-menu
COMMENTS